
Hemangiomas in muscle tissue can develop at any age, but most often occur in young adults. This angiogram image shows a hemangioma deep in the thigh. Hemangiomas in Muscle, Bone, and Internal OrgansĪlthough not as common as hemangiomas of the skin, hemangiomas do develop in other tissues, including muscle and bone. These hemangiomas are fully grown at birth and either completely involute during a baby's first year (called rapidly involuting congenital hemangioma), or they do not involute at all (called non-involuting congenital hemangioma). Hemangiomas that are present at birth (called congenital hemangioma), follow a different growth pattern. In addition, because these tumors can grow to be large and often appear on the face, neck, and scalp, a child's emotional needs must be considered when determining treatment options. However, some hemangiomas can cause problems with vital functions like breathing, eating, and seeing, and require some form of treatment. Most of these hemangiomas will shrink completely on their own and require no treatment. How long it takes for the tumor to reach full-size and then shrink varies greatly, but most infantile hemangiomas have finished involution by the time the child reaches puberty. Girls are affected slightly more often than boys.Ĭommon infantile hemangiomas follow the same growth pattern: a period of rapid growth, often during the first year, followed by a period of tumor shrinkage (called involution or regression). Most infant hemangiomas are capillary hemangiomas, although cavernous and compound types do occur.

They are sometimes present at birth, but most typically appear within the first weeks or months of life.
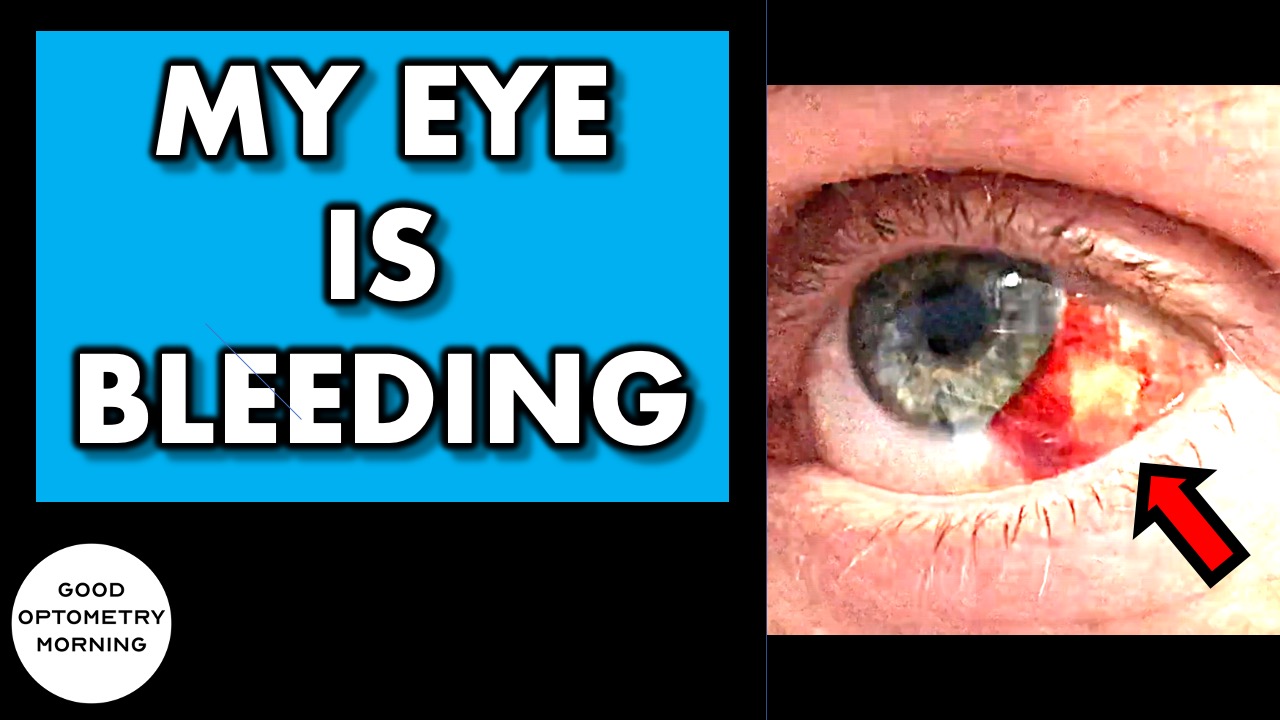
Burst blood vessel skin#
Hemangiomas of the skin are common in infants. This type of hemangioma is also sometimes referred to as a "pregnancy tumor" because they often appear during pregnancy, typically in the nose and mouth. Because they contain so many blood vessels, they bleed easily - often with just mild contact.

A hemangioma occurs when small blood vessels begin to multiply at an abnormal rate and form a mass or lump.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
